Tree trunk cutting methods for different product, applications and shapes
Wood is one of the most widely used materials in the world and is used in various industries.
Most people buy sawn wood, but few people are familiar with the process of timber production.
cutting wood
Cutting trees is the first step in wood production, and the final quality of wood depends on several factors such as the appearance, the structure of the tree in the forest, and the time it was cut. Each type of tree has a specific time to cut; For example, twenty years for an acacia tree, forty years for a birch tree, and eighty to two hundred years for an oak tree are considered appropriate times for cutting. If the tree is felled before the appropriate time, the resulting wood may be softer, more vulnerable to insects and prone to some physical defects.
On the other hand, if the tree is cut too late, the wood may be diseased or even rotten. Plant sap plays an important role in the growth and development of wood, and dead trees that have not yet been felled lose their value. To convert the pollinators into timber, they are sawed or quartered using methods that have the least amount of waste.
The most commonly used wood cuts
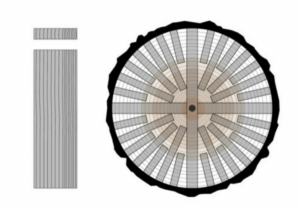
1.Rift Sawn
In this method, cutting is done perpendicular to the annual rings of the wood. This type of cutting allows the wood fibers to be seen well and the wood is less prone to twisting and longitudinal cracks. However, more wood is wasted compared to other cutting methods.

2.Quarter Sawn
In this method, cuts are made parallel to the four axes of the trunk. The pieces obtained are not twisted and annual rings are seen in large numbers and with full clarity.
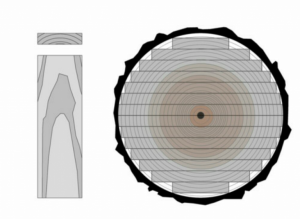
3.Flat Sawn/Live Sawn
Although the obtained parts are not of high quality due to having a percentage of wood core and soft wood, this method is still widely used. The central part, which overlaps with the core of the wood, may break, and other parts of the wood tend to bend as well.
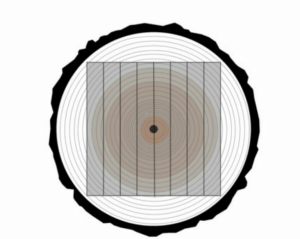
4.Parallel Boards
This method is very similar to Flat Sawn, but here the pieces are cut in smaller sections and therefore less likely to break and bend.
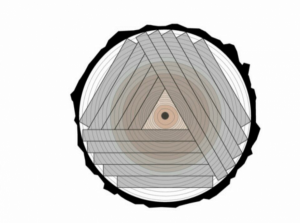
5.Cantibay Method
In this method, wider logs are produced and less wood is wasted, while the core of the trunk is also removed.
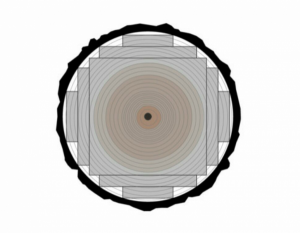
6.Whole Piece
In this method, by removing the bark, the maximum parts of the wood are used, and the final piece obtained is in the form of a square log.
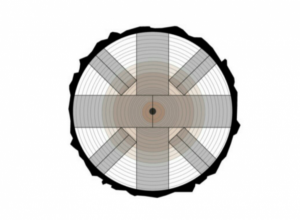
7.Cross Cut
In this method, by fully using the core of the wood, resistant pieces are produced and smaller pieces are cut from the remaining soft wood.

















































